What Is Genetic Makeup In Science
What is genetic modification (GM) of crops and how is it done?
GM is a technology that involves inserting Dna into the genome of an organism. To produce a GM found, new Dna is transferred into plant cells. Usually, the cells are and then grown in tissue civilization where they develop into plants. The seeds produced by these plants will inherit the new DNA.
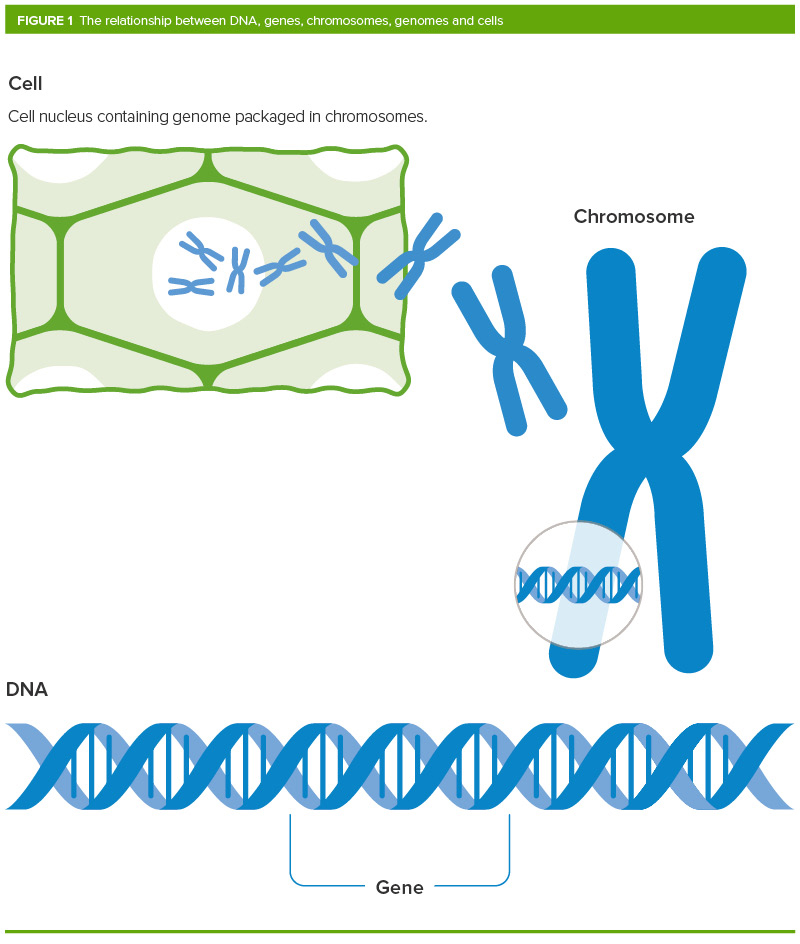
The characteristics of all living organisms are determined past their genetic makeup and its interaction with the environs. The genetic makeup of an organism is its genome, which in all plants and animals is made of Deoxyribonucleic acid. The genome contains genes, regions of DNA that ordinarily bear the instructions for making proteins. It is these proteins that give the plant its characteristics. For instance, the colour of flowers is determined by genes that conduct the instructions for making proteins involved in producing the pigments that colour petals.
Genetic modification of plants involves adding a specific stretch of DNA into the plant'due south genome, giving it new or dissimilar characteristics. This could include irresolute the way the plant grows, or making it resistant to a particular disease. The new Dna becomes part of the GM found's genome which the seeds produced by these plants will incorporate.
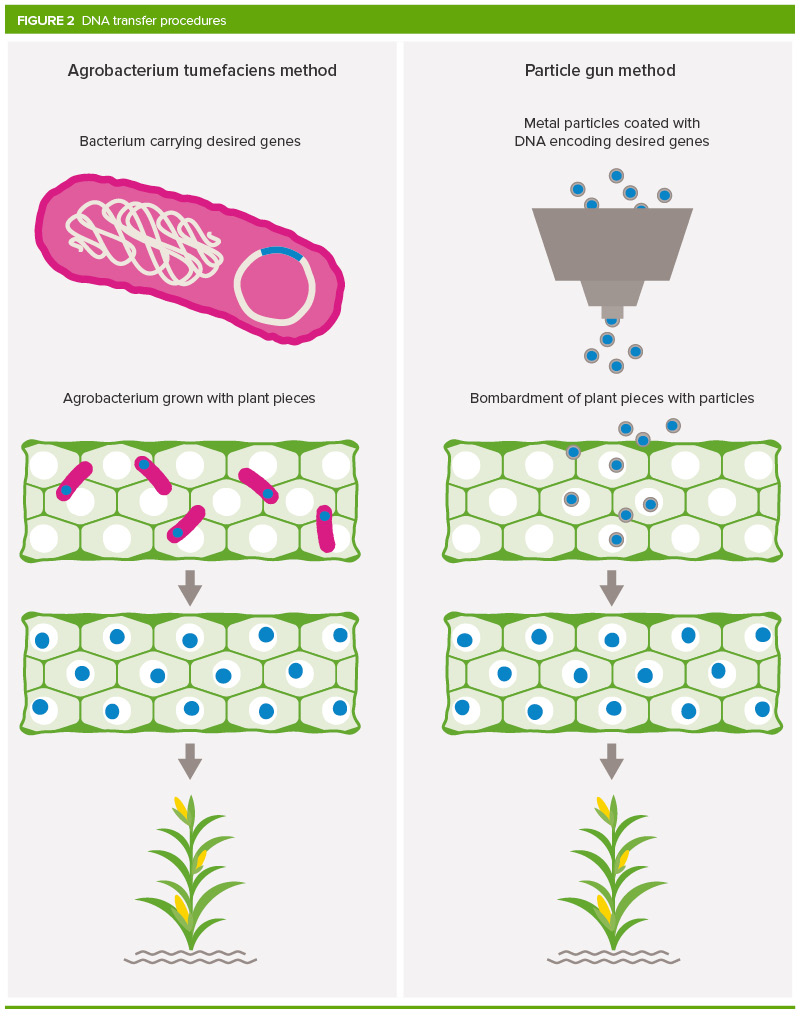
The get-go stage in making a GM plant requires transfer of DNA into a establish cell. One of the methods used to transfer DNA is to coat the surface of pocket-size metal particles with the relevant Deoxyribonucleic acid fragment, and bombard the particles into the constitute cells. Another method is to apply a bacterium or virus. In that location are many viruses and bacteria that transfer their Dna into a host cell equally a normal role of their life cycle. For GM plants, the bacterium almost oft used is called Agrobacterium tumefaciens. The gene of interest is transferred into the bacterium and the bacterial cells then transfer the new Dna to the genome of the plant cells. The found cells that take successfully taken upwards the DNA are then grown to create a new institute. This is possible because individual plant cells have an impressive capacity to generate entire plants. On rare occasions, the procedure of Dna transfer can happen without deliberate human intervention. For example the sugariness potato contains Dna sequences that were transferred thousands of years ago, from Agrobacterium bacteria into the sweet tater genome.
In that location are other ways to modify the genomes of crops, some of which are long established, such as mutational breeding, and others of which are new, such equally genome editing, but in this Q&A we are focusing on GM as information technology is currently commonly defined for regulatory purposes in Europe.
Meet related questions
- How mutual are genes in food?
- How does GM differ from conventional plant breeding?
- Who is paying for GM crop development and who owns the technology?
Folio last updated: May 2016
Download all questions and answers (PDF)
Source: https://royalsociety.org/topics-policy/projects/gm-plants/what-is-gm-and-how-is-it-done/
Posted by: burtonegary1949.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Is Genetic Makeup In Science"
Post a Comment